KCSE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1, 2 & 3 PREDICTION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS, KNEC REPORTS (KCSE PAST PAPERS LEAKAGE); GET ALL KCSE 2021-2022 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1,2 & 3 PREDICTION SETS DERIVED FROM TOP NATIONAL MOCKS AND KCSE PAST PAPERS
KCSE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 LEAKAGE DETAILS:
POLITE NOTICE: KINDLY NOTE THAT THE KCSE 2021-2022 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 LEAKAGE IN CIRCULATION IS FAKE. THE CABINET SECRETARY IN CHARGE OF EDUCATION CONFIRMED THAT THE UNIVERSITY STUDENT WHO WAS DISSEMINATING MISLEADING KCSE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 EXAM PAPERS HAS BEEN DETAINED AND IS AWAITING TRIAL.
Chemistry paper 1 is compulsory for all KCSE Knec-registered candidates. The paper carries a maximum of 80 marks and it majorly focuses on measuring the KCSE Candidate’s grasp of theoretical skills
KCSE Chemistry paper one generally tests the candidate’s ability to master theoretical concepts bordering on the study of matter- properties and reactions of matter.
HERE IS A FULL SET OF KCSE CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 PREDICTION QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS; TOP NATIONAL MOCKS & KCSE PAST PAPERS
Chemistry KCSE PAST PAPERS 1 2 & 3 per year-KCSE 2020 Chemistry Paper 1 Exam and Marking Scheme,
Paper-1-KCSE-2020-Marking-Scheme,
Chemistry KCSE PAST PAPERS 1 2 & 3 per year-KCSE 2020 Chemistry Paper 2 Exam and Marking Scheme,
Chemistry-Paper-2-KCSE-2020-Marking-Scheme,
Chemistry-Paper-2-KCSE-2020-Exam Chemistry,
Chemistry KCSE PAST PAPERS 1 2 & 3 per year-KCSE 2020 Chemistry Paper 3 Exam and Marking Scheme,
Chemistry-Paper-3-KCSE-2020-Exam,
Chemistry-Paper-3-Marking-Scheme-KCSE-2020,
Follow the links below to download free Chemistry KCSE past papers:
KCSE 2000 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2000 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2001 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2001 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2002 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2002 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2003 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2003 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2004 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2004 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2005 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2005 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2006 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2006 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2007 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2007 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2008 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2008 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2009 CHEMISTRY PAPER 1-E
KCSE 2009 CHEMISTRY PAPER 2-E
KCSE 2010 CHEMISTRY P1
KCSE 2010 CHEMISTRY P2
KCSE 2010 Chemistry P3
KCSE 2011 CHEMISTRY P1
KCSE 2011 CHEMISTRY P2
KCSE 2011 CHEMISTRY P3
KCSE 2012 CHEMISTRY P2
KCSE 2012 CHEMISTRY P1
KCSE 2012 CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS
KCSE 2013 Chemistry P1
KCSE 2013 Chemistry P2
KCSE 2013 Chemistry P3
KCSE CHEMISTRY QUESTIONS
More KCSE Papers
Differentiate between empirical and molecular formula (2mks)
The empirical formula shows the simplest whole-number ratio in which atoms combine to form a compound while the molecular formula shows the actual number of each kind of atoms present in a molecule of a compound.
Use the information below to answer the questions that follow Ethanol is formed as shown below
Use the information below to answer the questions that follow Ethanol is formed as shown below
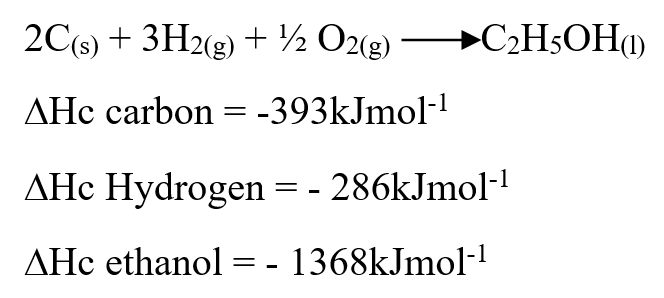
Draw the energy cycle diagram for the formation and combustion of ethanol and calculate the heat of formation of ethanol (3mks)
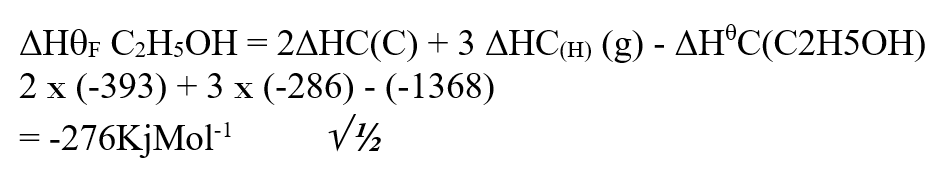
A volume of 80cm3 of a mixture of propane (C3H8) and oxygen was ignited in an experiment. The products were cooled and passed through aqueous sodium hydroxide. The final volume was reduced by 30cm3
a) Write the equation for the combustion of propane (1mk)
b) Determine the volume of;
i) The component of the original mixture (2mks)
ii) Residual oxygen (1mk)
State three differences between chemical and nuclear reactions.
a) State three differences between chemical and nuclear reactions. (3mks)
| Chemical reaction | Nuclear reaction |
| It takes place on the outer | Take place within the nucleus |
| Heat energy released is less | Heat energy released is large |
| Involves electrons | Involves neutrons and electrons |
| Affected by environmental factors | No affected by the environmental factors |
| such as temperature and pressure |
(any three 3mks)
b) Study the figure below and answer the questions that follow
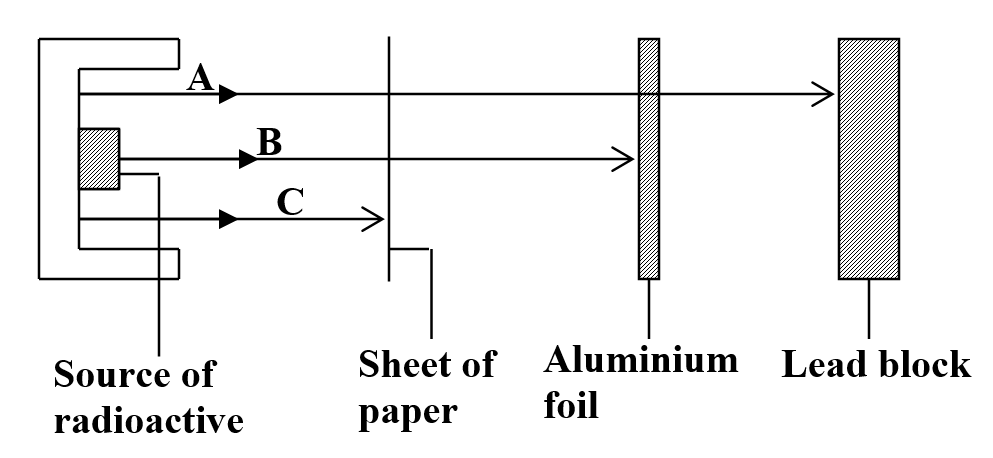
Identify the radiations A, B and C (3mks)
- A-Gamma rays
- B-Beta rays
- C-Alpha rays
RCOO – Na+ and RCH2OSO3 – Na+ represent two types of cleansing agents
11/10/2021
RCOO – Na+ and RCH2OSO3 – Na+ represent two types of cleansing agents
a) Name the class of cleansing agent to which each belongs (1mk)
b) Which one of the two cleansing agents is likely to pollute the environment. Explain. (2mks)
RCH2OSO3-Na+
Because it contains long chains of alkylbenzene and sulphate which is difficult to be broken by bacteria actionRead More
BELOW IS A SAMPLE OF CHEMISTRY PAPER ONE
KCSE CLUSTER TESTS 10
Chemistry Paper 1
1.
Describe the non–luminous flame of a Bunsen burner and give a reason why it’s preferred when heating substances in the laboratory. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. ………………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks2.
Study the diagram shown below to answer the questions that follow. The curve shows the heating curve of water in the laboratory.

i) At what temperature does the water boil? (1mark)
…..………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) Is the curve for pure water or impure water? Give a reason for your answer. (1mark) …………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
iii) Give the effect of impurities on the boiling point of water. (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks3.
Calcium carbonate reacts with dilute sulphuric VI acid to form a gas and a salt. i) Write an equation for the above reaction (1mark) ……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) Why would the above reactants not be suitable for the preparation of the above gas in the laboratory? (2marks) ……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks4.
Excess magnesium ribbon sample was heated in equal volumes of:-
i) Pure oxygen gas
ii) Air
a) Why was the mass of the resulting product in (ii) more than in (i)? (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
b) Write the equations for the reactions in part (ii) (2marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks5.
The set-up below was used to prepare dry hydrogen gas. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
i) Is the method of collecting the gas correct? Give a reason. (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) What would be liquid Y? (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
iii) Give two physical properties of hydrogen gas. (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks6.
Study the information tabulated below to answer the questions that follow

a) Write the electron arrangement of the
(i) Atom of Y ( ½ mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Ion of X ( ½ mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) Compare the ionic radius of Y with its atomic radius (2marks)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
5 marks7.
A student lowered burning magnesium in a gas jar of carbon (IV) oxide as shown in diagram

a) State and explain the observation made in the gas jar. (2marks)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) Write the equation of the reaction that takes place in the gas jar. (1mark) ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks8.
a) Using a dot (.) and cross (x) to represent the outermost electrons, draw diagrams to show the bonding in magnesium sulphide. (1 ½ marks)
b) State the structure of the above compound. ( ½ mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
c) Give two properties of substances with the above structure. ( ½ mks) …………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
3.5 marks9.
Given sodium carbonate solid, lead (II) nitrate solid and water, explain how you can obtain a solid sample of Lead (II) carbonate. …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks10.
a) State and explain the observations made when chlorine gas is bubbled through a solution of potassium bromide. (2marks) …………………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) Write the ionic equation for the reaction that took place in the above reaction. (1mark) …………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks11.
The diagram below shows part of the Solvay process.

a) Name solid X (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
b) State the process taking place in chamber L (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………
c) State two uses of sodium carbonate (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks12.
100cm3of methane gas diffused through a porous partition in 40 seconds. How long would it take 90cm3of ozone gas to diffuse through the same partition? C=12, H=1, O =16
3 marks13.
Calculate the volume of oxygen produced when 10g of silver nitrate was completely decomposed by heating at (s.t.p) (Ag =108, N=14, O = 16) Molar gas volume at s.t.p= 22.4dm3
3 marks14.
The scheme below shows some reactions starting with ethene. Study it and answer the questions that follow

a) Name substance
(i) X……………………………………..(1mark)
(ii) N…………………………………….( 1mark)
b) Name reagent M…………………………………………..( 1 mark)
c) Ethene undergoes polymerization to form a polymer. Give an equation for the reaction and name the product. (1 ½ marks) ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………
4.5 marks15.
Hydrogen sulphide gas was bubbled through a solution of zinc nitrate for some time. i) State the observation made. (1mark) ……………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………
ii) Where should the experiment be carried out and why? (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
iii) Write the equation of the reaction that occurs (1mark)
…………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………
3 marks16.
A solution of hydrogen chloride gas in water conducts an electric current, while that of hydrogen chloride in methylbenzene does not conduct. Explain. ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………… ………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 marks17.
The scheme below represents reactions starting with X solid
i) Identify solid X (1mark)
……………………………………………………………………………………….
ii) Write an ionic equation to show the formation of white precipitate. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
iii) Why would gas S not form a white precipitate with a solution of sodium hydroxide (1mark) ………………………………………………………………………………………..
……………………………………………………………………………………….. .
3 marks18.
The following results were obtained trying to determine the solubility of copper (II) sulphate in water at 400C. Mass of empty dish16.8g, mass of dish + saturated solution at 400C =26.9g, mass of dish + solid CuSO4 after evaporation to dryness = 17.8g. Calculate the mass of saturated solution containing 70g of water at 400C.
3 marks19.
When 16g of ammonium nitrate was dissolved in 100cm3 of water at 250C, the temperature of the solution drops to 190C. a) Calculate the molar enthalpy of solution of ammonium nitrate (3mk)
(N = 14, O= 16, H=1 Specify heat capacity of water =4.2kJkg-1k-1)
b) Is the enthalpy change endothermic or exothermic? Give a reason (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks20.
Ammonia gas was passed into the water as shown below.

a) What is the use of the inverted funnel. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
b) Explain why the pH of the solution is above 7. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
2 marks21.
The set-up below was used to carry out the electrolysis of lead bromide. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
a) Identify electrodes U and T. (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
b) Identify with reason one missing condition in the above set-up. (2marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks22.
a) Name the following compounds
2 marks23.
25cm3 of 0.12M Potassium Hydroxide solution required 30cm3 of a solution of a dibasic acid (H2X) for complete neutralization. The acid contained 3.15g per 500cm3 solution. Calculate
(i) The molarity of the acid solution. (2marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) The relative molecular mass of the acid. (2marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
4 marks24.
A mixture of ammonium chloride and sodium nitrate was heated together in a round-bottomed flask to produce gas X.
i) Identify gas X ( ½ marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
ii) Write equations to show how gas X is formed. (2marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
iii) Why would gas X not be collected over cold water? ( ½ marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks25.
Solid P when heated gives a black powder Q and a colourless gas that forms a white precipitate in lime water. When dilute Sulphuric (VI) acid is added to the powder Q, a pale blue solution is formed.
a) Give the chemical formula of i) Solid P (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
ii) Solid Q (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
iii) Write an equation for the reaction that takes place (1mark)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks26.
In an experiment, sulphur (IV) oxide gas was bubbled into the water followed by chlorine gas. The resulting colourless solution gave a while precipitate when mixed with barium chloride solution. Explain these observations.
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks27.
5.0g of calcium carbonate were allowed to react with 25cm3 of 0.1M hydrochloric acid until there was no further reaction. Calculate the mass of calcium carbonate that remained unreacted. (Ca =40, C= 12,O=16) (3marks)
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………..
3 marks
BELOW IS A SAMPLE OF CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 MARKING SCHEME
KCSE CLUSTER TESTS 16
Chemistry Paper 1 Marking Scheme
1.
PAPER 1
1.
(ii) Electronic configuration 5 :8:2

(iii)Both atoms are period 3. X has a larger atomic radius than Y√ ½. Since Y has a higher nuclear charge ⁄⁄ more protons√ ½.
4 marks2.
(a) It is the exchange of ions during a chemical reaction resulting in the formation of an insoluble salt and a soluble salt.
(b)To solution of sodium sulphate add lead II nitrate solution. Filter √ ½ the precipitate and wash it with distilled water. The precipitate is √ ½ 4 PSO.

3 marks3.

.(b) Each has a molecular of 44. Hence diffuse at the same rate under similar conditions.√ 1
3 marks4.

3 marks5.
(a) bleaches by reduction(removal of Oxygen)in presence of sunlight. Oxygen is replaced.
(b) Calcium bisulphate.
(c) It removes Sulpher (IV) Oxide from the air thus reducing the pollution.
4 marks6.
(a) Equilibrium shifts to the left favouring backward reaction and green colour are increased.
(b) Forward reaction favoured equilibrium shifts to the right and yellow colour dominates.

2 marks7.

(b). Nuclear fission-process by which leavings nuclide split when bombarded by a fast-moving neutron. In the process, energy is released. Nuclei at high velocity. In the process, energy and neutrons are released.
4 marks8.
(i)Fractional crystallization.


3 marks9.

(ii) Addition polymerisation.
2 marks10.
(i) Heating.
(ii) To absorb ⁄⁄ dissolve Hydrogen chloride fumes.
(iii) By Downward delivery tube⁄⁄upward displacement of air.
4 marks11.
(a) Silicon dioxide ⁄⁄ 2 SiO ⁄⁄silicon IV oxide and Aluminium oxide ⁄⁄ 3 2OAl.
(b) Provide carbon IV oxide ⁄⁄ 2 CO that reacts with coke to release CO which is a reducing agent.
―Provide Calcium oxide ⁄⁄ CaO that removes impurity silica as Calcium silicate.
3 marks12.
(a) Residue is yellow when hot, white on cooling: Brown fumes formed.

(b)Gas A is Oxygen.
3 marks13.

3 marks14.
(a) Lowers the melting point.
(b) Cleaning of ice from roads.
―Extraction of metals.
3 marks15.
Both fully lionises in water ⁄⁄ strong acid-strong base recast ion). Ammonium hydroxide partially ionises and therefore energy is used up to ionise them completely.
2 marks16.
(a) Concentrated sulphuric acid dehydrates sugar to form black carbon.
(b) Oxygen in the air, in the presence of sunlight replaces the Oxygen removed from the material during bleaching.
2 marks17.
(a) The volume of a fixed mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure at a constant temperature.

(c) When volume is decreased at a constant temperature, gas particles have a shorter distance before colliding with each other and the walls of the container. The collisions become more frequent which increased pressure.
2 marks18.

(ii) Sample B.Has temporary hardness which can be removed by precipitating from soluble hydrogen carbonates as Insoluble carbonates
2 marks19.
(i) Increases the electrical conductivity of water by providing more free ions.
(ii)
2 marks20.
At high temperatures, water molecules have higher Kinetic energy-thus increasing the frequency of collision of the molecules with magnesium.
2 marks21.
(a) M in the box with atomic number11.
(b) R in the box with atomic number 7
2 marks22.
Reducing power increase from lithium to caesium.
This is due to the increase in atomic size which puts the outermost electron further away from nuclear charge hence easily lost.
2 marks23.
(a)Dissolve the mixture in ether and filter to remove camphor. They dissolve the residue in ethanol to remove sugar.
The residue after filtering is Alum.
(b)Dissolve the mixture in ether and filter to remove camphor as the filtrate. Dissolve the residue in ethanol and then filter to set Alum. The filtrate is a sugar solution. Evaporate it to its dryness to set sugar.
4 marks24.
(a)Chloride Oxidises Sulphide ions to pale-yellow sulphur and itself reduced to hydrochloric acid.
(b)
2 marks25.
(a) Mass of salt A that forms crystals when cooled
Mass of salt B that forms Crystals when cooledHence total mass
(b)Its solubility would increase with an increase in temperature because it requires heat to dissolve (the endothermic process is favoured by high temperature.
2 marks26.
(a) . ,2,1 ane dibromoeth
(b)Ethanol.
(c) . Ethane
3 marks27.
(a) (i)Zinc atoms ⁄⁄. Zn 3
(ii)Silver ions ⁄⁄. Ag
(b) The blue colour of the solution fades, there is arise in temperature ⁄⁄ apparatus feel warm, A brown/ red solid deposited.
3 marks28.
Mixture sulphur power with warm Carbon disulphide.
―Filter the mixture.
―Allow the filtrate to evaporate slowly at room temperature.
―Pale yellow octahedral crystals are formed.

2 marks29.
(a) Behaviour where a substance shows both acidic and basic properties.
(b) .
(c)M is a stronger acid than L. It ionizes fully producing more hydrogen ions which react to give more hydrogen gas than L.
2 marks